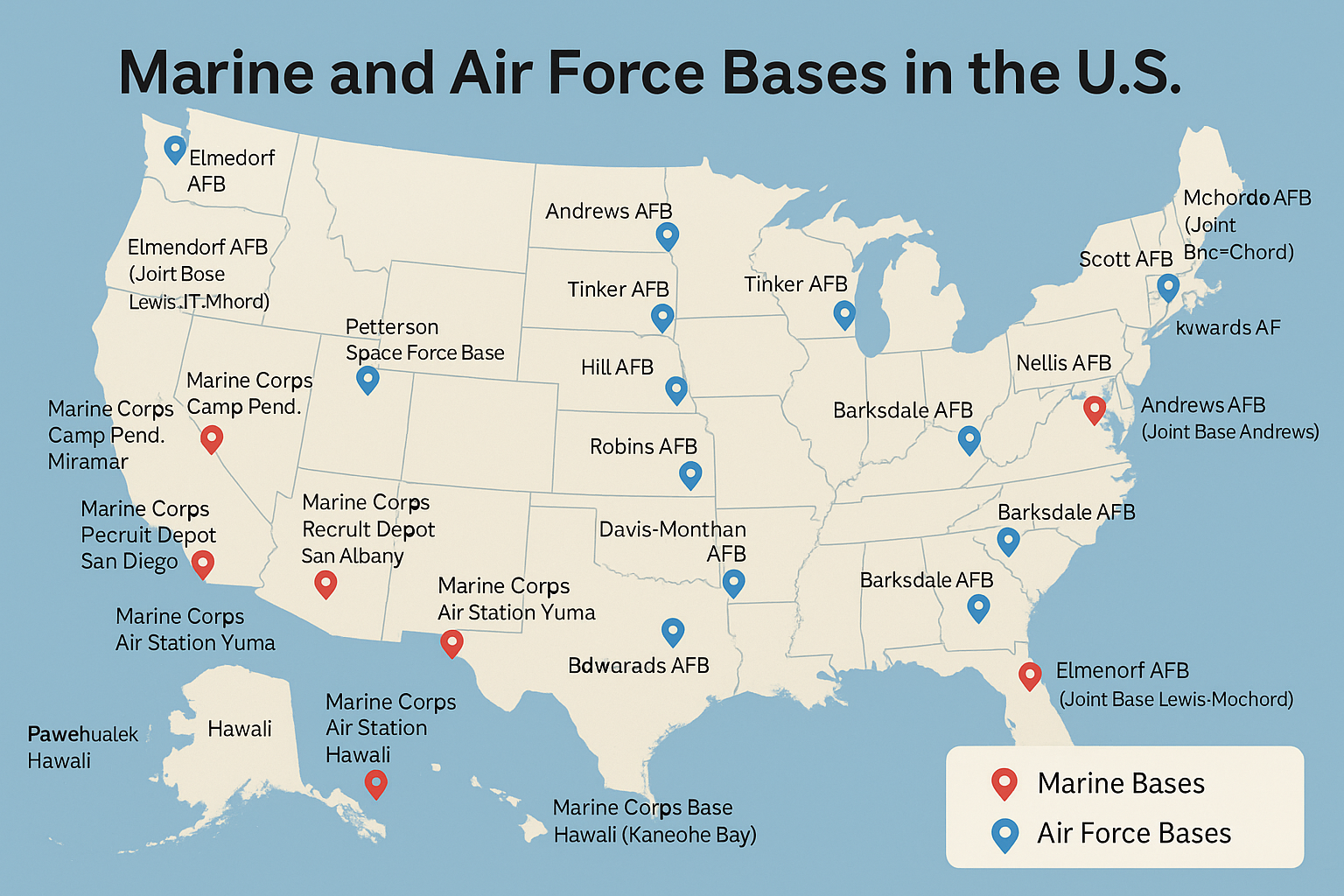
🛡️ All U.S. Marine and Air Force Bases: Complete Guide to America’s Military Strongholds
🏁 Introduction
The United States military operates one of the most sophisticated and geographically diverse systems of bases in the world. From deserts to coastlines, urban zones to isolated islands—each base plays a vital role. This article covers every major Marine Corps and Air Force base in the U.S., offering details about their missions, functions, and why they remain cornerstones of national defense.
🎯 Importance of Military Bases in the U.S.
Military bases aren’t just clusters of runways and barracks—they’re hubs of strategy, technology, logistics, and combat readiness. They serve as:
- Training centers
- Logistics hubs
- Deployment launching points
- Intelligence and cyber warfare centers
- Emergency disaster response nodes
Each branch—Marine Corps and Air Force—has bases tailored to their specific missions, but all are linked by one goal: protecting national interests at home and abroad.
🪖 Marine Corps Bases in the United States
The United States Marine Corps (USMC) is a rapid-response, amphibious warfare branch. Its bases reflect this mission: mobility, discipline, and deployment capability.
🌍 Key Marine Installations by Region
| Marine Base | Location | Specialization |
|---|---|---|
| Camp Pendleton | California | Amphibious operations, West Coast hub |
| Camp Lejeune | North Carolina | East Coast operations, amphibious readiness |
| Quantico | Virginia | Officer training, education, FBI Academy |
| Twentynine Palms | California | Live-fire combat training |
| Parris Island | South Carolina | Marine Recruit Training (East) |
| San Diego MCRD | California | Marine Recruit Training (West) |
| MCAS Miramar | California | Marine aviation |
| MCAS Yuma | Arizona | Desert warfare aviation |
| MCAS Beaufort | South Carolina | Fighter aircraft and F-35 training |
| MCB Hawaii | Kaneohe Bay, Hawaii | Pacific operations & amphibious defense |
🏋️♂️ Training and Mission Focus
Marine bases emphasize:
- Basic and advanced combat training
- Urban and desert warfare drills
- Expeditionary readiness
- Logistics support and prepositioning of equipment
✈️ Air Force Bases in the United States
The U.S. Air Force (USAF) is the backbone of American air superiority and technological dominance. With over 60 major bases in the continental U.S., its reach is vast.
🧠 Command Centers and Research Bases
| Air Force Base | Location | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Wright-Patterson AFB | Ohio | Research, logistics, and innovation hub |
| Edwards AFB | California | Flight testing and NASA partnership |
| Peterson Space Force Base | Colorado | NORAD, space and satellite defense |
| Hanscom AFB | Massachusetts | Cyber and electronic systems |
🚀 Operational Air Force Bases
| Air Force Base | Location | Aircraft/Function |
|---|---|---|
| Eglin AFB | Florida | Weapons testing |
| Lackland AFB | Texas | Basic training |
| Nellis AFB | Nevada | Air combat training |
| Scott AFB | Illinois | Mobility and communications |
| Tinker AFB | Oklahoma | Maintenance and aircraft depot |
| Hill AFB | Utah | Fighter logistics |
| Davis-Monthan AFB | Arizona | A-10 operations and aircraft boneyard |
| Elmendorf AFB | Alaska | Arctic air defense |
| Andrews AFB | Maryland | VIP transport and Air Force One |
🔍 Differences Between Marine and Air Force Installations
| Factor | Marine Corps | Air Force |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Ground and amphibious warfare | Air and space superiority |
| Base Layout | Infantry-centric, smaller airstrips | Runways, hangars, advanced tech centers |
| Training Facilities | Recruit depots, combat zones | Flight simulators, cyber warfare centers |
| Deployment | Often rapid and temporary | Strategic global deployment and support |
🧭 Strategic Roles of Each Branch’s Bases
- Marine Corps Bases: Enable rapid assault, amphibious landing, and infantry training.
- Air Force Bases: Provide intelligence, mobility, precision airstrikes, and nuclear deterrence.
Together, they ensure global force projection and homeland security.
Department of Defense Base Structure Report
📊 Interactive Table: Major Marine and Air Force Bases
| Branch | Base | State | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marine Corps | Camp Lejeune | NC | Amphibious Warfare |
| Marine Corps | Camp Pendleton | CA | Training & Deployment |
| Air Force | Wright-Patterson AFB | OH | Research & Development |
| Air Force | Nellis AFB | NV | Combat Readiness |
| Air Force | Lackland AFB | TX | Basic Training |
| Marine Corps | MCAS Miramar | CA | Marine Aviation |
💼 Impact of Military Bases on Local Economies
Military installations often support tens of thousands of civilian jobs. They stimulate:
- Local housing markets
- Small businesses (retail, restaurants, services)
- Infrastructure (schools, hospitals)
- Tax revenues and tourism
For example, Camp Lejeune contributes over $6 billion annually to North Carolina’s economy.
💡 Technological Innovation at U.S. Air Force and Marine Bases
Both branches invest heavily in cutting-edge defense technology, including:
- Autonomous drones and AI systems
- Hypersonic weapons development
- Cybersecurity defense labs
- Satellite and space launch operations
USAF bases like Edwards AFB and Wright-Patterson AFB are on the frontier of defense tech.
❓ FAQs
1. How many Marine Corps bases are there in the U.S.?
There are around 15 major Marine Corps bases located across the U.S., not counting Reserve and smaller installations.
2. Which is the largest Marine base in the U.S.?
Twentynine Palms (MCAGCC) in California is the largest Marine Corps base by land area.
3. How many Air Force bases are in the United States?
There are over 60 major Air Force bases across the continental U.S., with additional installations in Alaska, Hawaii, and overseas.
4. Can civilians visit these military bases?
Some bases offer public tours, but access is generally restricted. Special clearance or sponsorship is often required.
5. Are all bases still active?
Not all. Some are inactive or decommissioned, while others have been repurposed or merged into joint bases (e.g., Joint Base Andrews).
6. What’s the difference between a Joint Base and a normal base?
A Joint Base is shared by multiple military branches (e.g., Air Force and Army), like Joint Base Lewis-McChord in Washington.
✅ Conclusion
U.S. Marine and Air Force bases are far more than military outposts. They are strategic power centers, deeply embedded in the nation’s defense, economy, and innovation ecosystem. Whether it’s a jet roaring from a runway in Alaska or Marines training in the California desert, these bases define readiness, resilience, and reach.